
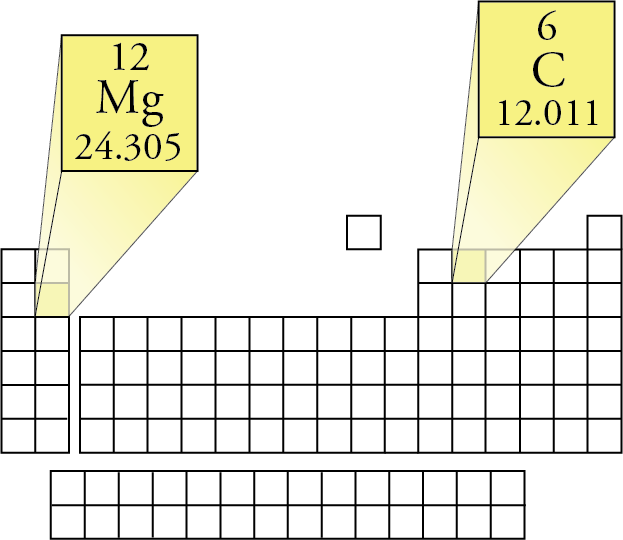
One can determine the relative atomic frequencies of a composition by the compound’s molecular formula. To find the molar mass of a molecule or an ionic compound, all one has to do is first multiply the molar masses of the constituent elements by their frequency in the compound, and add the total values together. So, hydrogen has a molar mass of 1.00794 g/mol that is, 6.0221476 × 10 23 hydrogen atoms would together weigh 1.00794 grams. To find the molar mass of hydrogen, we simply multiply this number by the molar mass constant to get 1.00794 g/mol. Hydrogen, for instance, has a standard atomic weight of 1.00794. The molar mass of any element can be determined by multiplying that elements standard atomic weight (listed on the periodic table) by the molar mass constant M u=1g/mol. a measure of how much mass one mole of that element has. Credit: “Mole” Andi via Flickr CC BY-SA 2.0Įvery element has a molar mass, i.e. Just like the words “million” and “billion,” the word “mole” stands for a specific quantity of things approximately 602,214,150,000,000,000,000,000 of them. 1 mole is defined as an amount of substance that contains exactly 6.0221476 × 10 23 constituent particles. The measure of molar mass (g/mol) is based on the SI unit for quantity, the mole (not to be confused with the cute burrowing mammal). In chemistry, molar mass is understood as a physical property that is defined as the mass of a substance divided by the amount of that substance. The molar mass of a given substance is a quantitative measure that tells you the mass of 1 mole of that substance. One mole of glucose molecule has a mass of 180.16 g. Glucose has a molar mass of 180.16 g/mol. In one molecule of glucose, there are 12 hydrogen, 6 carbon, and 6 oxygen atoms. Glucose is composed of hydrogen (H), carbon (C), and oxygen (O) The molar mass of H is 1.0079, the molar mass of C is 12.0107, and the molar mass of O is 15.9994. The molar mass of glucose can be calculated by multiplying the molar masses of its atomic constituents by their frequency in a single molecule and adding those values together. You’ll be a little groggy, a little grumpy.” - Jack LaLanne And when you go on a low-carb/high-protein diet, your brain is using low-octane fuel. “The brain’s preferred source of fuel is glucose/carbohydrates.
Glucose provides the raw materials needed for cellular respiration and the production of ATP. Glucose is normally stored in the body in the form of starch or glycogen. Glucose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) and is the most abundant carbohydrate. Glucose (C 6H 12O 6) is an organic macromolecule that is essential for the metabolism of essentially all eukaryotic organisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
